What is Fluid? Types of Fluid? How does fluid flow? Types of flow? Laminar | Turbulent | Compressible | Incompressible
What is fluid?
Anything which can flow is called fluid like liquids and gas because of its weak intermolecular forces.

What are Static and Dynamic fluid?
Static fluid: A fluid at rest is known as static fluid, it has no shear stress.
Dynamic fluid: A fluid that is in motion is known as dynamic fluid.
Example: Take a glass of water when the water in the glass is not moving, it is a static fluid. When you move the glass in a circular motion the water inside it starts moving or rotating. It is a dynamic fluid. River is an example of dynamic fluid. A pond is settled water that is a static fluid.
How does a fluid flow?
Fluid flows due to two reasons:
- Difference between pressure
- Difference between potential energy
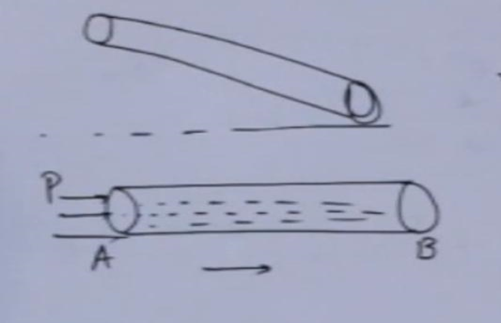
Types of flow
- Steady and unsteady flow
- 1D, 2D, 3D flow
- Laminar and turbulent flow
- Uniform and non-uniform flow
- Compressible and incompressible flow
1. Steady and unsteady flow:
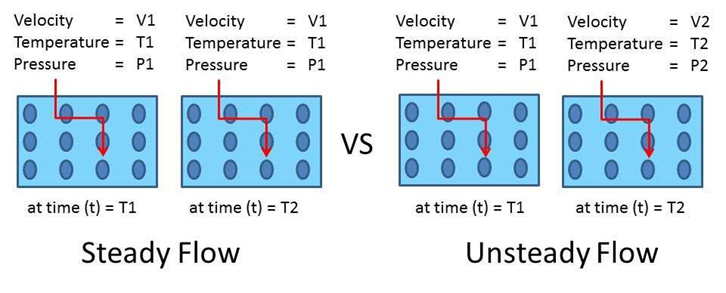
Steady flow is defined as the type of flow in which fluid characteristics like velocity, pressure, density, etc. at a point do not change with time.
Unsteady flow is a type of flow in which the velocity, pressure, and density at a point change with time.
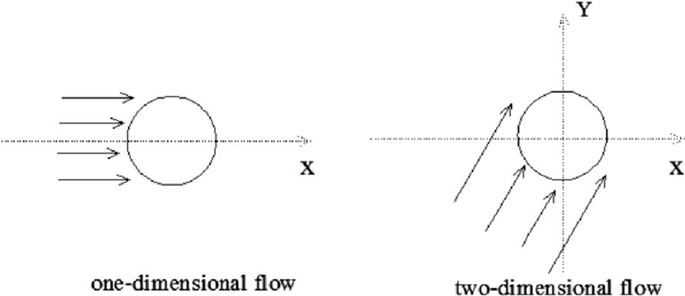
2. 1D, 2D, 3D flow
1D flow is a type of flow in which the flow parameter such as velocity is a function of one space coordinate only. The variation of velocities in the other two mutually perpendicular directions is assumed negligible.
2D flow is a type of flow in which velocity is a function of two space coordinates only. The variation of velocity in the third direction is negligible.
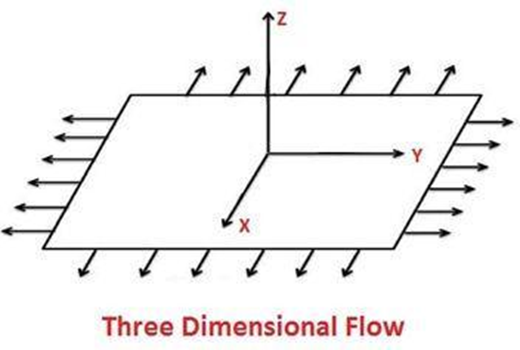
3D flow is the type of flow in which velocity is a function of three mutually perpendicular directions.
3. Laminar and turbulent flow:
A flow of fluid where each particle of fluid follows a smooth path, paths which never interfere with one another, and the velocity of the fluid is constant at any point in the fluid is called laminar flow.
Turbulent flow is an irregular flow where the velocity of a fluid is not constant at every point. In the case of turbulent flow liquid flowing in the pipe has no fixed speed or direction.
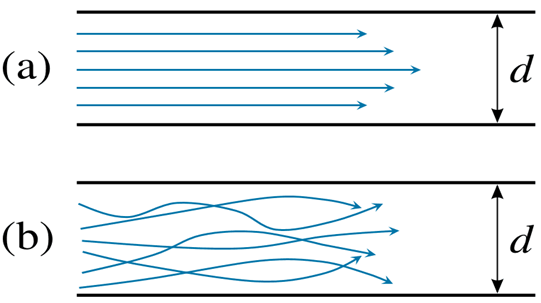
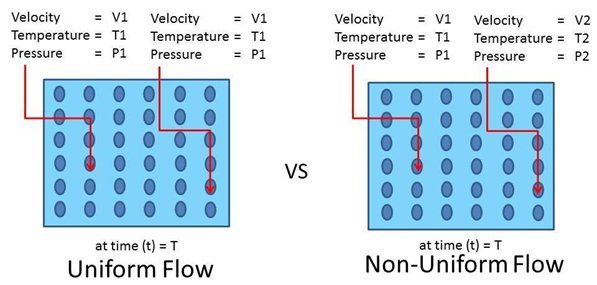
4. Uniform and non-uniform flow
Uniform flow is defined as the type of flow in which the velocity at any given time has the same magnitude and direction. Non-uniform flow is the type of flow in which velocity changes from time to time at any given instant of time.
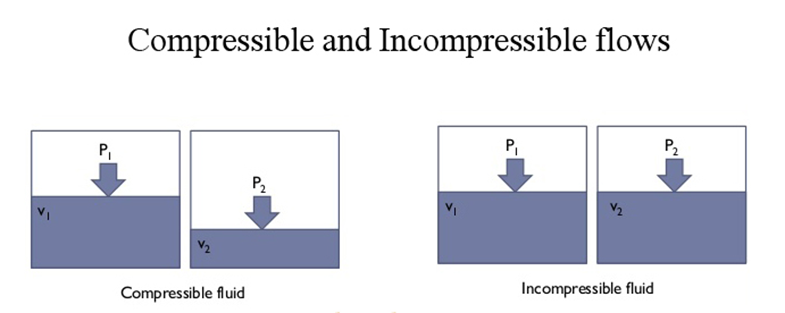
5. Compressible and incompressible flow
Compressible flow is the type of flow in which the density of the fluid changes from point to point. In other words, density is not constant like in gases. Incompressible flow is the type of flow in which the density does not change from point to point. In other words, density is constant, Generally, liquids are incompressible.
Note:
If you want to learn more about this topic, we suggest checking out our Combo package with the given link https://www.merchantnavydecoded.com/courses/c/ . It’s a great way to dive deeper into the subject through video explanations. This package covers all the important details and presents them in an easy-to-understand format. Watching the videos will help you grasp the topic better and make learning more enjoyable. So, we highly recommend giving our Combo package a try to enhance your knowledge on the subject.
Disclaimer :- The opinions expressed in this article belong solely to the author and may not necessarily reflect those of Merchant Navy Decoded. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information provided and disclaim any responsibility for it. Data and visuals used are sourced from publicly available information and may not be authenticated by any regulatory body. Reviews and comments appearing on our blogs represent the opinions of individuals and do not necessarily reflect the views of Merchant Navy Decoded. We are not responsible for any loss or damage resulting from reliance on these reviews or comments.
Reproduction, copying, sharing, or use of the article or images in any form is strictly prohibited without prior permission from both the author and Merchant Navy Decoded.



[…] the help of the rotatory motion of the pump which produces dynamic action on fluid to move the fluid that is called a rotodynamic […]
[…] centrifugal pump is a mechanical device that is used to transport fluids by converting rotational kinetic energy into hydrodynamic energy for fluid flow. The rotational […]
[…] Definition: In fluid dynamics, Bernoulli’s theorem states that the total energy of moving fluid consisting of the gravitational potential energy of the elevation, the energy associated with the fluid pressure and the kinetic energy of the moving fluid is constant. In simple terms, it is the relation between pressure, velocity and elevation of moving fluid. […]