Top 10 Navigational Equipments Onboard
Introduction
Ship navigation apparatus consists of several instruments and units intended to allow sailors to find their location and figure out a way to get to their destination, avoid obstacles, and float safely. These equipments enhance the safety of the ship, the crew, and the cargo aboard.
If you want to learn amazing and informative videos about ships like Tanker, then check out our Tanker Familiarization Course.
1:- Global Positioning System (GPS) on Ship
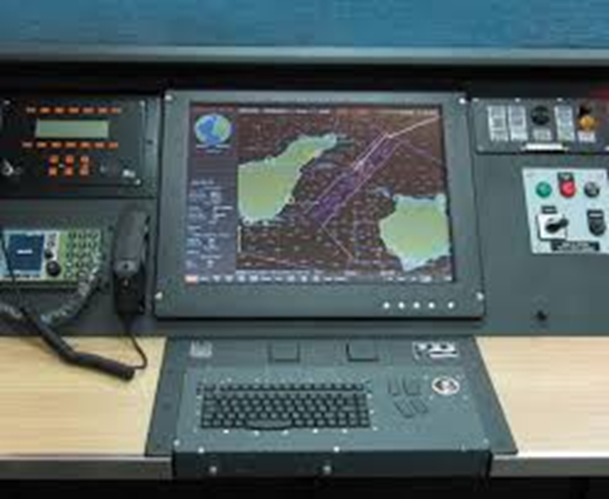

- GPS stands for Global Positioning System.
- It provides the ships with a precise location on Earth and, therefore, aids them in safe navigation.
- With GPS satellites, it can track the position of a given receiver on Earth.
- These units, being the satellites, send information to GPS devices installed on ships.
- The emissions watcher displays the readings, indicating latitude, longitude, and other important parameters.
- GPS not only allows the sailors to plan their routes and track their trips but also to locate themselves in the oceans.
- It can be seen as a virtual chart of the oceans, which is used by ships.
2:- Radar Systems of Ship

- A radar system on ships helps detect other vessels, landmasses, and obstacles, especially in poor visibility conditions like fog, rain, or darkness.
- The radar sends out radio waves from an antenna. These waves bounce off objects and return to the radar.
- The radar calculates the distance and direction of the objects based on the time it takes for the waves to return and the direction from which they return.
- Key components include the antenna, transmitter, receiver, and display.
- The antenna rotates to send and receive radio waves in all directions. The transmitter generates the radio waves while the receiver captures them.
- The display shows the radar image, indicating the position of objects around the ship.
- It helps in collision avoidance by detecting other vessels and by identifying storms and heavy rains.
- Radar systems work on 2 bands X-Band and S-Band depending on the need and situation the ship is in.
3:- Electronic Chart Display and Information Systems (ECDIS)
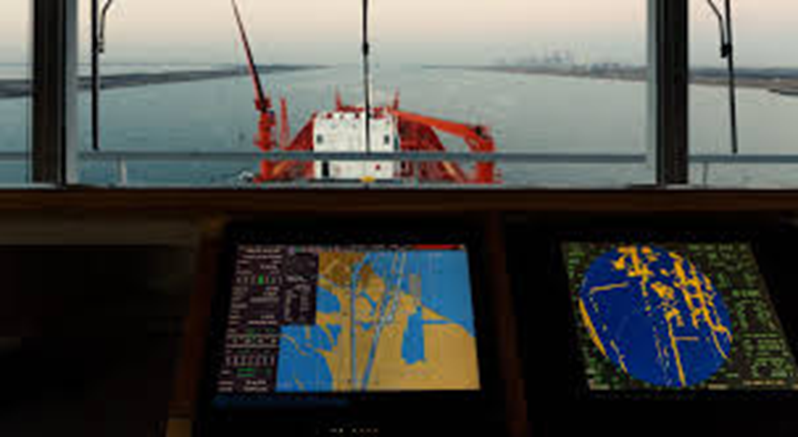

- ECDIS is a computerized navigation system that uses electronic charts for real-time positioning of the vessel. It has replaced traditional paper charts with digital versions.
- Seafarers may utilize it to navigate across the route and avoid any dangers, e.g., obstacles or insufficient depth.
- ECDIS also indicates other vessels and helps to avoid collision.
- It’s like an additional or more enhanced app for a smart GPS that is used by sailors to keep them safe.
- ECDIS, in turn, sends the information updated in real-time to the sailors. Sailors will always have the relevant information available to them.
- In brief, ECDIS is an essential tool for the navigation of a vessel as it allows sailors to make it to their destination, at least, without being at risk.
4:- Automatic Identification System (AIS)

- AIS (Automatic Identification System) is a device mounted on vessels to give information to signal-receiving stations about the broadcasting ships.
- The Automatic Identification System provides information like the positions, speed, course, name, CTA, and the identity of the vessel.
- AIS (Automatic Identification System) helps manage smooth water traffic and allows ships to dock without interfering with each other.
- Handheld devices use VHF radio towers to transmit and receive messages.
- AIS performs advanced tasks and, after each operation, sends data about the vessel’s status.
- Boats and shore stations with AIS receivers, in addition to their radars, can display this information.
- To conclude, AIS provides key support in ensuring the safety of ship routing and optimizing performance procedures as it provides real-time data about the position and identification of the vessel in the sea.
5:- Gyro Compass in Ship
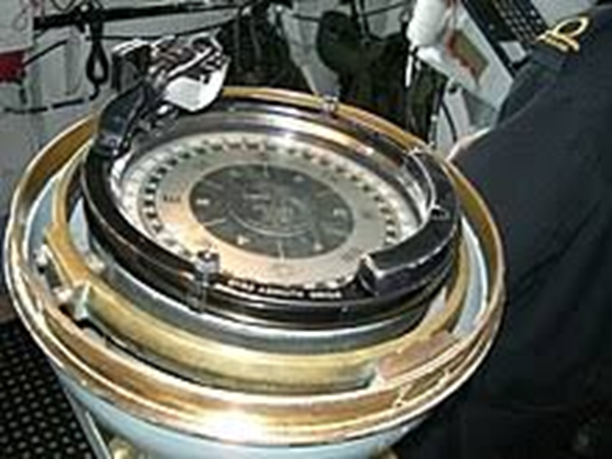

- It functions by revolving along the axis of the Earth instead of moving in the opposite direction like the rest of the celestial bodies.
- Unlike magnetic compasses, gyroscopes do not rely on magnetism but rather use complex mechanisms, which is what makes them unaffected by magnetic fields and thus more reliable.
- They always generate correct dead reckoning data regardless of whether the ship is moving or whether its magnetic field is interfered with by some device.
- They are there to keep the sailor steering in the right direction as the ship moves forward safely and accurately.
- A gyrocompass is one of the essential equipment for ships to do that. Without gyrocompasses, the ships can’t stay on course and reach the target.
6:- Echo Sounder Onboard Ship
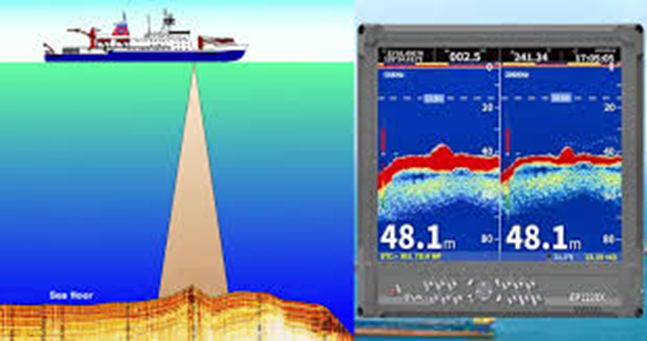
- The depth sounder, or what many know as the echo sounder, is very significant equipment for navigating the sea safely without posing any threat to the vessel.
- They form a set of pulses, and after sending them down into the water, they register how long it takes for them to come off.
- This gives the sailor a reading that indicates the relation of the water to the ship’s bottom.
- The echo signal is displayed on a screen and measured by a depth sounder, indicating the water depth or any obstacles under the water.
- Sailing in the ocean is like having a giant book in which chart-makers write about sea depth and any potential dangers like rocks or reefs. These data are very useful for sailors to avoid unexpected events in the ocean.
- When navigating shallow water or unknown underwater terrain, depth sounders are crucial so that the sailor can be alert.
7:- Rudder Angle Indicator
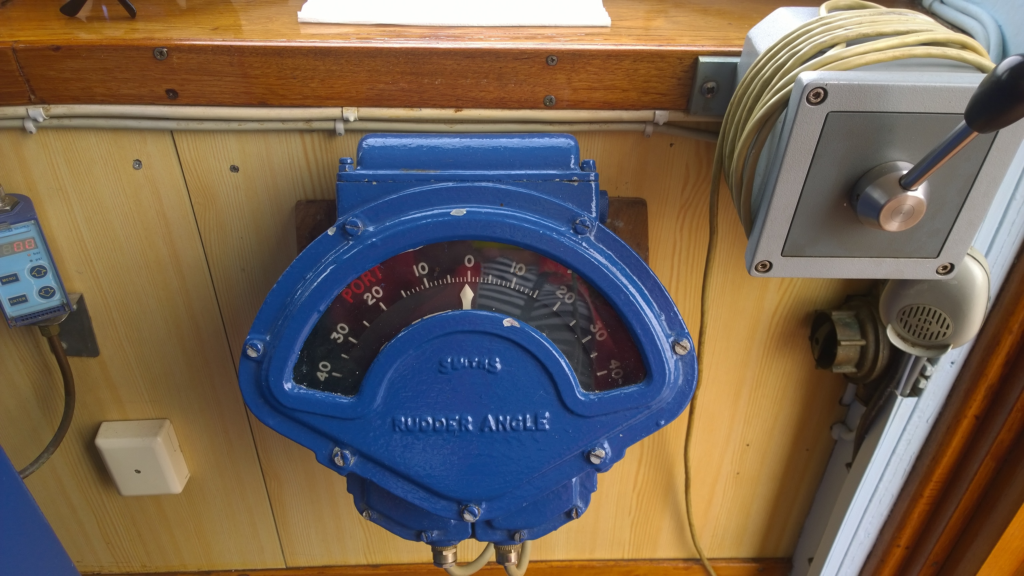

- The rudder angle indicator shows how far the ship’s rudder is turned from the center. This helps the crew steer the ship accurately.
- You can find these indicators on the ship’s bridge, in the engine room, and in the steering gear room. This way, important crew members can always check the rudder’s position.
- There are two kinds: mechanical and electronic. Mechanical ones use cables to connect to the rudder, while electronic ones use sensors to send data to a display.
- Knowing the exact rudder angle is crucial for maneuvers like docking, sailing through narrow areas, or avoiding obstacles. It ensures the ship moves exactly as needed.
- The indicator helps keep the ship safe by preventing too much rudder movement, which can cause oversteering or loss of control, especially in bad weather.
- Modern indicators often work with the ship’s autopilot and navigation systems. It makes the steering smoother and safer whether it’s done by a person or automatically.
8:- Voyage Data Recorder (VDR)

- The Voyage Data Recorder (VDR) is an equipment that is mandatory to be put on the ship and collects all necessary data concerning the voyage.
- Being able to store data such as location, speed, heading, and connecting with other ships continuously, it functions just like a black box in aviation.
- For purposes of finding the reasons for an accident or incident, experts use VDR data to understand and improve safety measures.
- VDRs help in the analysis of accidents, post-mortem analysis, and general compliance with international maritime laws and standards.
9:- Automatic Radar Plotting Aid (ARPA)
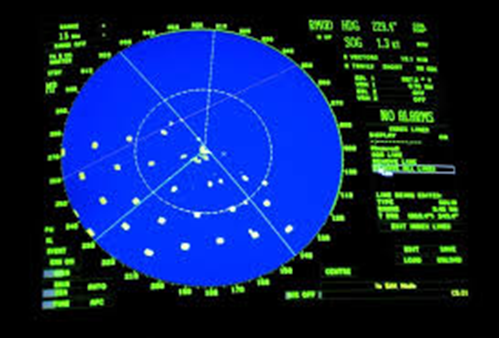
- ARPA stands for Automatic Radar Plotting Aid. It is a radar system that identifies and foretells other vessels’ locations in the sea.
- It makes matters more clear and easier to see by illustrating the tracks and moves of neighboring ships for their vessel.
- ARPA helps in crash risk calculation and provides alarms to alert the crew to potential dangers. This system is crucial in preventing collisions at sea.
- This ultimately improves navigational safety for all involved parties.
- ARPA systems on commercial ships, especially in crowded waterways and busy shipping lanes, greatly facilitate the work of navigators. These systems significantly enhance the overall safety of life and property at sea.
10:- Weather Routing Systems
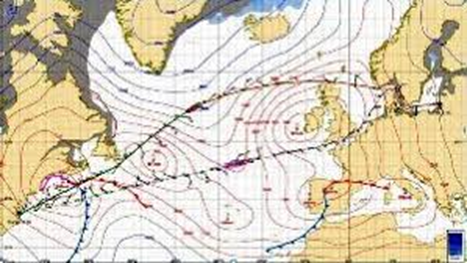
- Navigators assess weather forecasts, sea conditions, wind, and currents to determine the most effective route. It ensures the voyage is both efficient and secure by carefully evaluating these factors.
- There is the use of weather routing systems that result in optimal fuel consumption, save time on the journey, and limit the days spent inside huge storms.
- The systems, by sending regional weather updates and course recommendations in time, directly affect safer and more efficient maritime processes.
Conclusion
The navigating gear on ships is the backbone of all ocean voyages, enabling sailing in an effective manner and their success. With GPS, Navaids, ECDIS, AIS, and dynamic positioning systems, sailors can navigate the seas with ease. These advanced tools provide them with all the necessary information and capabilities for safe and efficient navigation. As the maritime makes its rounds of inclination, quality navigation equipment has to constantly be available to establish it as a reliable component of modern maritime operations.
Disclaimer :- The opinions expressed in this article belong solely to the author and may not necessarily reflect those of Merchant Navy Decoded. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information provided and disclaim any responsibility for it. Data and visuals used are sourced from publicly available information and may not be authenticated by any regulatory body. Reviews and comments appearing on our blogs represent the opinions of individuals and do not necessarily reflect the views of Merchant Navy Decoded. We are not responsible for any loss or damage resulting from reliance on these reviews or comments.
Reproduction, copying, sharing, or use of the article or images in any form is strictly prohibited without prior permission from both the author and Merchant Navy Decoded.



